Google Login
Author(s)
- Bishwanath Jana
- Ayan Ghosh
Last Updated Date
2025-08-11
SRS References
- 2.1.2 (External Authentication)
Version History
| Version | Date | Changes | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 2025-08-11 | Initial draft for Google Login | Bishwanath Jana |
| 2.0 | 2025-08-12 | Initial draft for Google Login | Bishwanath Jana, Ayan Ghosh |
Feature Overview
Objective:
Enable users to authenticate via Google using the ID token validation flow. The client obtains a Google ID token through Google OAuth and sends it to IAMService. IAMService validates the token through multiple security checks, verifies the user exists in our system, then issues an access token (returned in response body) and refresh token (set as HttpOnly cookie). This implementation follows a secure validation process that ensures only legitimate, existing users can authenticate.
Scope:
Backend authentication endpoint with comprehensive token validation. New login endpoint in IAMService that validates Google ID tokens and authenticates existing users only. No automatic user creation. Reuse existing JWT issuance and refresh-cookie logic. Optional domain restriction (Google Workspace).
Key Security Features:
- Multi-step token validation (signature, audience, issuer, expiration, email verification)
- Existing user validation (no automatic account creation)
- Secure token distribution: Access token in response body, Refresh token in HttpOnly cookies
- Comprehensive error handling and rejection of invalid requests
Dependencies:
- Google Identity Platform (ID token issuance on the client)
- NuGet: Google.Apis.Auth (ID token validation)
- IAMService existing auth components: IAuthHelper, CookieHelper, DeviceTypeIdentifier, LoginResponse, MbdnStatusCode
- Configuration keys: Google:ClientId (required), Google:HostedDomain (optional)
Requirements
- Provide a new POST /google-login endpoint (IAMService.AuthController) with AllowAnonymous.
- Accept body:
{ idToken: string (required), userType?: UserType }. - Validate ID token using GoogleJsonWebSignature.ValidateAsync with Audience = Google:ClientId; enforce issuer and expiration.
- Token Validation Process:
- Verify token signature and structure
- Check
aud(audience) claim matches configured Google:ClientId - Check
iss(issuer) claim is from Google (accounts.google.com or https://accounts.google.com) - Check
exp(expiration) claim to ensure token is not expired - Require
email_verified= true in payload - Optionally enforce Google:HostedDomain match when configured
- User Lookup and Validation:
- Find existing user by email from the validated token payload
- If user does not exist in the system, reject the request with appropriate error message
- Do not create new users automatically during Google login process
- Issue access token and a new refresh token for validated existing users only.
- Token Response Strategy:
- Return access token in the response body as part of LoginResponse
- Set refresh token via HttpOnly cookie using CookieHelper
- Do not include refresh token in response body for security
- Return the standard LoginResponse payload with access token on successful authentication.
- Error Handling:
- Invalid token → Return 400 Bad Request
- Token validation failure (aud/iss/exp/email_verified) → Return 400 Bad Request
- User not found → Return 400 Bad Request with "User does not exist" message
- Server errors → Return 500 Internal Server Error
- Add audit logging and apply existing rate limiting to this endpoint.
- Add configuration keys: Google:ClientId (required), Google:HostedDomain (optional).
- Non-functional: enforce security validations, maintain performance comparable to other login calls, provide observability (metrics/logs), and preserve backward compatibility.
Detailed Authentication Flow
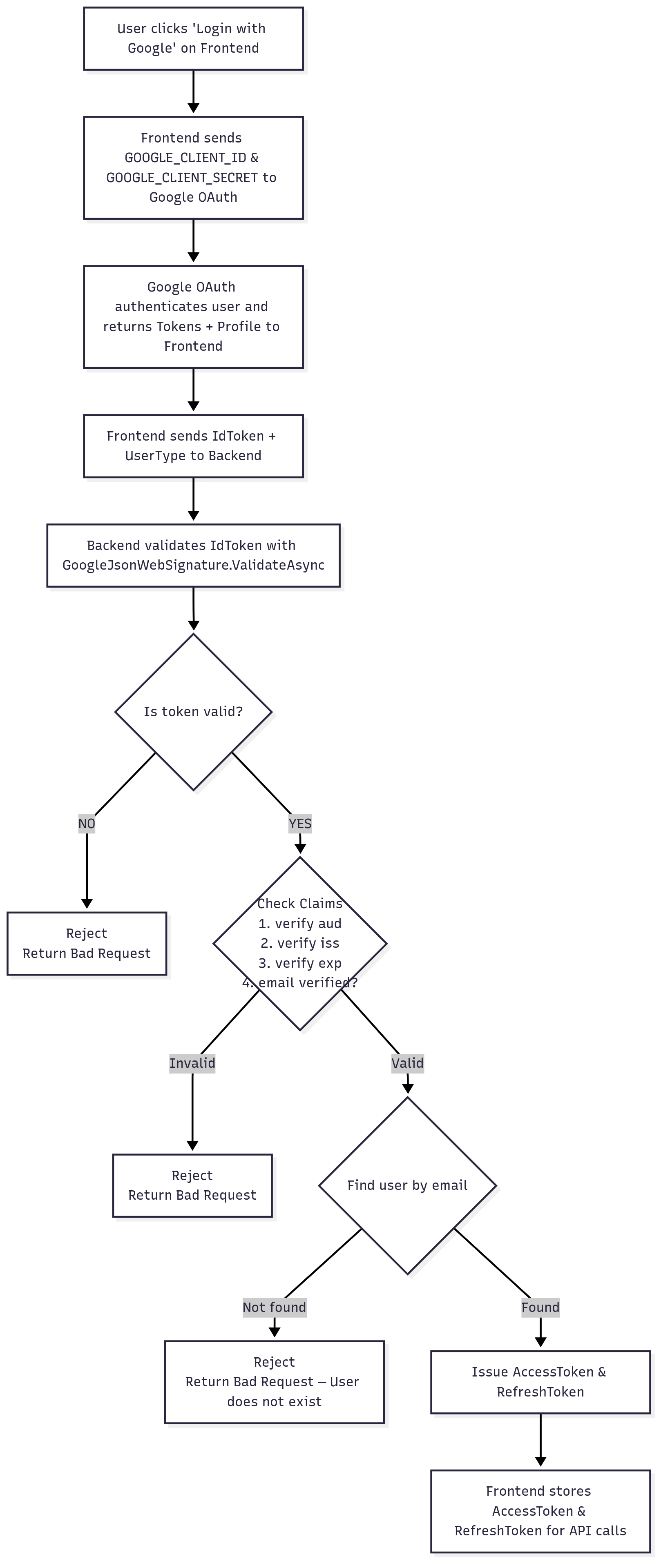
Based on the flowchart implementation, the Google authentication follows these specific steps:
Phase 1: Frontend Google OAuth
- User clicks 'Login with Google' on Frontend
- Frontend initiates Google OAuth with GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID & GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
- Google OAuth authenticates user and returns Tokens + Profile to Frontend
Phase 2: Token Transmission
- Frontend sends IdToken + UserType to Backend via POST /google-login
Phase 3: Backend Validation
Step 1: Token Validation
Backend validates IdToken with GoogleJsonWebSignature.ValidateAsync
├─ Valid Token → Continue to Claims Check
└─ Invalid Token → Return 400 Bad Request
Step 2: Claims Verification
Check Claims:
├─ Verify 'aud' (audience) matches configured Google:ClientId
├─ Verify 'iss' (issuer) is from Google
├─ Verify 'exp' (expiration) - token not expired
└─ Verify 'email_verified' = true
├─ All Valid → Continue to User Lookup
└─ Any Invalid → Return 400 Bad Request
Step 3: User Existence Check
Find user by email:
├─ User Found → Issue Tokens
└─ User Not Found → Return 400 Bad Request "User does not exist"
Step 4: Token Issuance & Response
Issue AccessToken & RefreshToken:
├─ Return AccessToken in LoginResponse body
├─ Set RefreshToken in HttpOnly Cookie
└─ Frontend receives AccessToken in response, RefreshToken stored securely in cookie
Design Specifications
This section details the backend contract and integration points. UI is out of scope.
-
UI/UX Design:
N/A (Backend-only feature) -
Data Models:
External identity model and request DTO used by the endpoint.// Request DTO
public sealed class GoogleLoginRequest
{
public string IdToken { get; set; } = default!;
public UserType? UserType { get; set; } // Optional; default decided by server policy
}
// External identity descriptor
public sealed class ExternalIdentity
{
public string Provider { get; set; } = "Google";
public string ProviderUserId { get; set; } = default!; // Google "sub"
public string Email { get; set; } = default!;
public string? Name { get; set; }
} -
API Interfaces:
Endpoint for Google ID token exchange.Endpoint Method Parameters Response Response Status Codes /google-loginPOSTBody: idToken(required, string),userType(optional, enum)LoginResponse200,400,401,500 -
Third-Party Integrations:
- Google Identity Platform (ID Token JWTs)
- NuGet: Google.Apis.Auth (token validation)
-
Workflow:
- User Initiates Login: User clicks 'Login with Google' on Frontend
- Google OAuth Setup: Frontend sends GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID & GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET to Google OAuth
- Google Authentication: Google OAuth authenticates user and returns Tokens + Profile to Frontend
- Token Transmission: Frontend sends IdToken + UserType to Backend
- Token Validation: Backend validates IdToken with GoogleJsonWebSignature.ValidateAsync
- Validation Decision:
- If token is invalid → Reject and return Bad Request
- If token is valid → Proceed to claims verification
- Claims Verification: Check Claims:
- Verify
aud(audience) - Verify
iss(issuer) - Verify
exp(expiration) - Verify
email_verified= true
- Verify
- Claims Decision:
- If any claim is invalid → Reject and return Bad Request
- If all claims are valid → Proceed to user lookup
- User Lookup: Find user by email in the system
- User Existence Decision:
- If user not found → Reject and return Bad Request with "User does not exist" message
- If user found → Issue tokens
- Token Issuance: Issue AccessToken & RefreshToken
- Token Response:
- Return AccessToken in response body (LoginResponse)
- Set RefreshToken as HttpOnly cookie
- Frontend stores AccessToken from response body for API calls
Development Tasks & Estimates�
| No | Task Name | Estimate (Hours) | Dependencies | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add NuGet Google.Apis.Auth to IAMService | 0.5 | NuGet feed | Restore/build |
| 2 | Add config keys (ClientId, HostedDomain) | 0.5 | App settings | All envs |
| 3 | Add DTOs and helper signatures | 1.0 | ContractLibrary | Request/ExternalIdentity |
| 4 | Implement comprehensive token validation logic | 3.0 | Google lib | aud/iss/exp/email_verified |
| 5 | Implement AuthController /google-login endpoint | 2.0 | Validation logic | Request handling + error mapping |
| 6 | Implement user lookup and existence validation | 2.0 | DAL | Email-based user lookup |
| 7 | Implement token issuance for existing users only | 2.0 | Auth helpers | No user creation logic |
| 8 | Tests (unit + integration) | 2.5 | Test framework | Mock Google validate + all flows |
| Frontend Tasks | ||||
| 9 | Create google login service function | 2.0 | ||
| 10 | Implement google login profile callback | 2.0 | ||
| 11 | Create google login button in login page and implement google login | 2.0 | ||
| Total | 19.5 |
Testing & Quality Assurance
-
Unit Tests:
- Valid Flow: Valid token + existing user → success; access token in response body and refresh token cookie set
- Token Validation Failures:
- Invalid token signature → 400 Bad Request
- Wrong audience (
aud) → 400 Bad Request - Wrong issuer (
iss) → 400 Bad Request - Expired token (
exp) → 400 Bad Request - Email not verified (
email_verified= false) → 400 Bad Request
- User Validation:
- Valid token + user not found by email → 400 Bad Request with "User does not exist"
- Valid token + existing user → successful authentication with access token in body
- Domain Restrictions: Hosted domain mismatch (when configured) → 400 Bad Request
-
Integration Tests:
- End-to-end call to
/google-loginwith mocked Google validator, verify LoginResponse and cookie flags across environments. - Verify refresh token rotation behavior.
- Test complete authentication flow from frontend Google OAuth to backend token validation.
- End-to-end call to
-
Acceptance Criteria:
- Given a valid Google ID token for an existing user, API returns 200 with LoginResponse containing access token and sets refresh token as HttpOnly cookie.
- Given an invalid token (any validation failure), API returns 400 Bad Request and does not set cookie or return access token.
- Given a valid token for non-existing user, API returns 400 Bad Request with "User does not exist" message.
- When HostedDomain is configured and mismatched, request is rejected with 400 Bad Request.
- All token validation steps (aud, iss, exp, email_verified) are enforced correctly.
- Access token is only returned in response body, never in cookies.
- Refresh token is only set as HttpOnly cookie, never in response body.
-
Testing Tools:
- xUnit/NUnit (unit tests), Moq/NSubstitute, Postman/REST Client, Application Insights/Serilog for logs
Deployment Considerations
-
Configuration Changes:
- Add to IAMService appsettings:
Google:ClientId(required),Google:HostedDomain(optional) - Configure secrets per environment; do not store secrets in repo
- No feature flag required
- Add to IAMService appsettings:
-
Rollout Plan:
- Deploy IAMService after config keys are present
- Smoke-test
/google-loginin each environment - Monitor failures; rollback by reverting the service version if needed
-
Optional Schema Change:
- If not already present, consider an
ExternalLogintable to store provider links:- Columns: Id (PK), UserId (FK), Provider (nvarchar), ProviderUserId (nvarchar), CreatedAt
- Unique index on (Provider, ProviderUserId)
- If not already present, consider an
Risks & Mitigations
| Risk | Impact | Likelihood | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invalid token acceptance | High | Low | Multi-step validation: signature, aud, iss, exp, email_verified checks |
| Token replay attacks | High | Low | Enforce expiration validation and token uniqueness |
| Unauthorized user creation | High | Very Low | Removed: Only existing users can authenticate via Google login |
| Account enumeration via login | Medium | Low | Generic error messages; rate limiting; audit logging |
| Domain policy bypass | Medium | Low | Enforce HostedDomain when configured; test negative cases |
| Cookie misconfiguration | Medium | Medium | Validate HttpOnly/Secure/SameSite per environment; integration tests |
| Rate limiting gaps | Medium | Medium | Apply existing auth rate-limits; monitor failed attempts |
| User not found attacks | Low | Medium | Generic error handling; avoid revealing system user information |
Review & Approval
-
Reviewer:
Ayon Das -
Approval Date:
2025-08-12
Notes
- Frontend/UI integration is out of scope here; clients should use Google Identity Services to obtain ID tokens.
- Reuse existing JWT and refresh token flow to minimize client-side changes.
- Consider adding metrics for attempts/success/failure to improve observability.